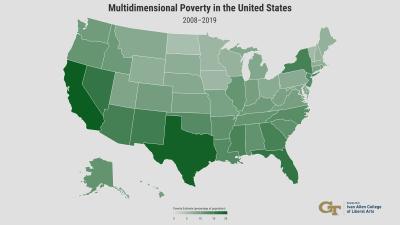
New research from Associate Professor Shatakshee Dhongde in Georgia Tech’s School of Economics finds that people living in California, Texas, and Florida were more likely than other U.S. residents to experience multiple forms of deprivation, such as lack of access to healthcare or affordable housing. These multiple deprivations combined to push many into a state of poverty that has not been picked up in official income-based measures.
Dhongde's paper, written with co-author Robert Haveman at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, is her latest in a series of work on the topic and the first to break down multidimensional poverty on a state-by-state level over more than a decade.
"This is important because there was much variation across states in how the Great Recession and the following recovery affected the multidimensional poor," Dhongde said. "Now we can apply those lessons to Covid recovery efforts to help ensure the policies are as effective as possible and reaching the people who need it the most."
Geographic and demographic breakdown
Analyzing data from 2008 to 2019, the researchers found that multidimensional poverty increased across the United States during the Great Recession from 2008 to 2010 and gradually declined through 2019.
The analysis showed that poverty among adults aged 18 to 65 was most widespread in the South and West. At the peak of the Great Recession in 2010, 20% of adults in Florida — more than two million people, according to census reports — were experiencing at least two measures of deprivation. In Texas, 22% of adults, totaling nearly 3.5 million people, were multidimensionally poor. However, the highest rate of multidimensional poverty was in California, where more than 5.5 million adults — nearly one in every four — were multidimensionally poor in 2010.
In the North, New York stood out as an exception with a high rate of multidimensional poverty. At the same time, states such as Iowa, Minnesota, North Dakota, and Vermont had some of the lowest multidimensional poverty rates, at 5% to 6% of the population.
According to the researchers, the high multidimensional poverty rate in California, Texas, and Florida is partially explained by their large Hispanic populations. Hispanics living in the United States are significantly more likely to experience two or more measures of poverty than other demographic groups, Dhongde and Haveman found. On average, they wrote, white people in the United States had the lowest multidimensional poverty rate at 10.4 percent, Black people and Asians had moderate rates at 14.8 and 16.5 percent, respectively, and Hispanics experienced the highest multidimensional poverty rates at 34.7 percent.
Little overlap with income deprivation
Surprisingly, the researchers found that having an income below the poverty line and experiencing multidimensional poverty (living with at least two of the six alternative deprivations) did not significantly overlap. According to the research, 13% of adults were multidimensional poor, and about 12.5% were income poor. However, there was a small overlap between the two groups; only 5.5% were both income poor and multidimensional poor.
Of the six deprivations studied, most multidimensional poor lacked health insurance and a high school education. They also faced a severe housing cost burden. “This underscores our argument that income poverty often fails to capture deprivation in other dimensions affecting the quality of life,” Dhongde and Haveman wrote.
Less surprisingly, “among individuals who were not income poor, deprivation was highest when individuals had incomes just above the poverty threshold,” the researchers found. They recommend expanding policies to help individuals living just above the poverty line as well as those below it to help reduce multidimensional poverty in the U.S.
Translating these lessons to Covid-19
The researchers also noted that immigrants were four times more likely to be multidimensionally poor than those born in the United States, and that multidimensional poverty rates were highest among children and young adults, single-parent families, and immigrants. Dhongde and Haveman speculate that these population groups are also the most likely to be socially and economically affected by the Covid-19 pandemic.
“In coming years, as the country recovers from the pandemic, it will be even more important to monitor multidimensional poverty in conjunction with income poverty in order to get a better idea of the impact on the quality of life experienced by a country’s population,” they wrote.
Spatial and Temporal Trends in Multidimensional Poverty in the United States over the Last Decade was published in Social Indicators Research: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-022-02902-z.
The article is the latest in Dhongde's body of literature on the topic, which includes studies on multidimensional poverty during the Covid pandemic, during the Great Recession, among senior citizens, and across racial and ethnic groups. Her work has been featured on NPR, in US News and World Report, Public Health Post, How Stuff Works, and many other outlets.